Xinyu Li, University of Washington.
Table of Links
- Abstract and Introduction
- 2. Method and 2.1. G is constant
- 2.2. Linear Relation between G and I
- 2.3. Nonlinear Quadratic Relation between G and I
- 3. Results
- 4. Conclusion and References
2. Method
The Keynesian cross model builds upon two ordinary differential equations [6]:

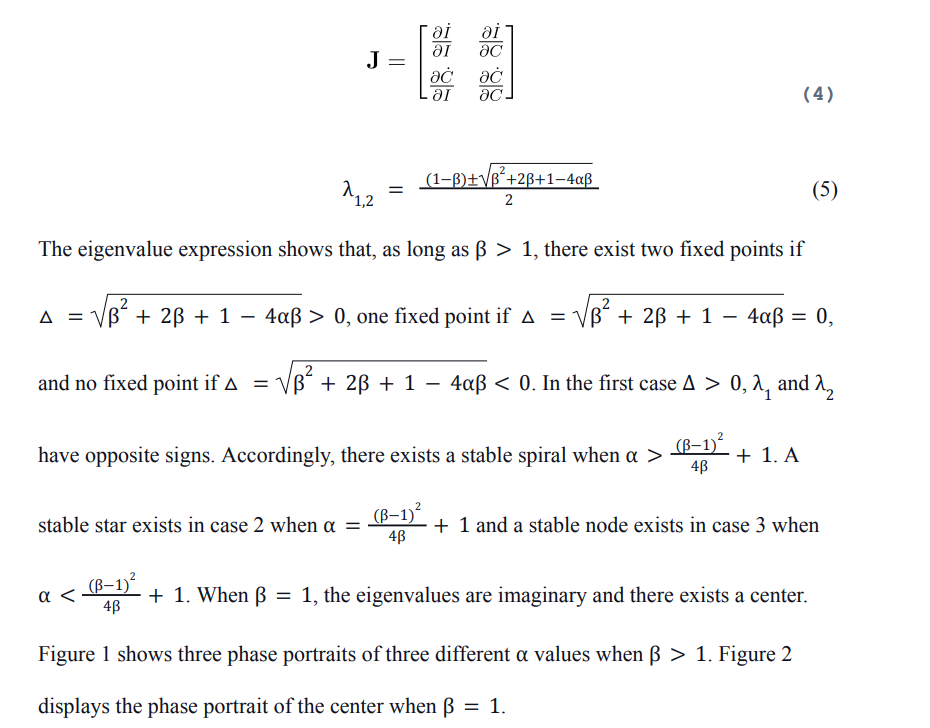
where C ≥ 0 is the rate of consumer spending, I ≥ 0 is the national income, and G ≥ 0 is the rate of government spending. The parameters α and β satisfy 1 < α < ∞, 1 ≤ β < ∞. Three relations between government spending and national income are discussed in the following subsections.
2.1. G is constant
Consider a model consisting of equations (1) and (2) along with a constant government spending G. To determine the equilibrium state for this model, I find the point where = Ċ = 0. Rearranging terms, I obtain the following equilibrium:

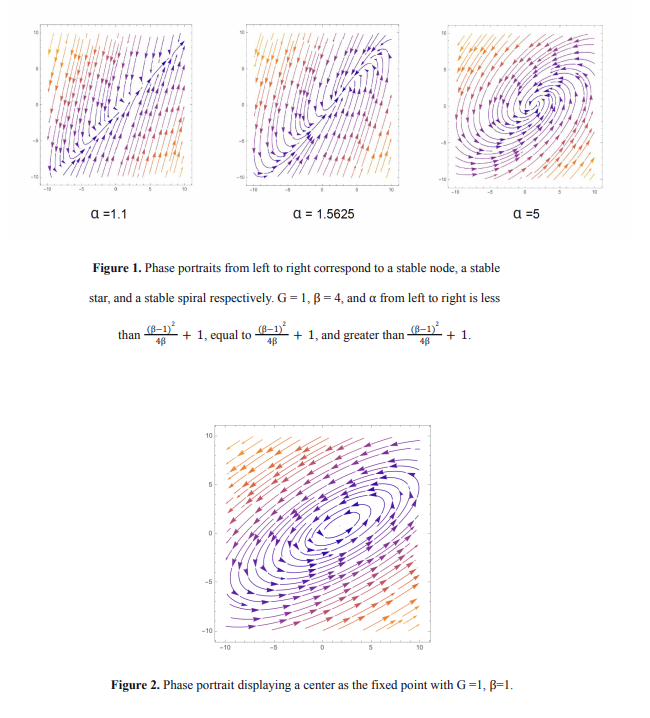
In order to calculate the stability of this fixed point, I compute the Jacobian matrix and eigenvalues:
This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license.